-
The idea of INCOTERMS (international commercial terms) was first proposed in 1921 by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). The first version of INCOTERMS, prepared by BTR specialists, was published in 1936 and was valid for about 20 years. Some additions and changes to the document were made in 1967, 1976, 1980, 1990, 2000. The latest version of the document "INCOTERM 2010" came into force on January 1, 2011.
What is Incoterms?
International rules in dictionary format, providing unambiguous interpretations of the most widely used trade terms in the field of foreign trade of a private nature, primarily in relation to the free - place of transfer of responsibility from the seller to the buyer. International trade terms are standard terms of international sales contracts that are defined in advance in an internationally recognized document, in particular, are used in the standard sales contract developed by the International Chamber of Commerce.
Group by function
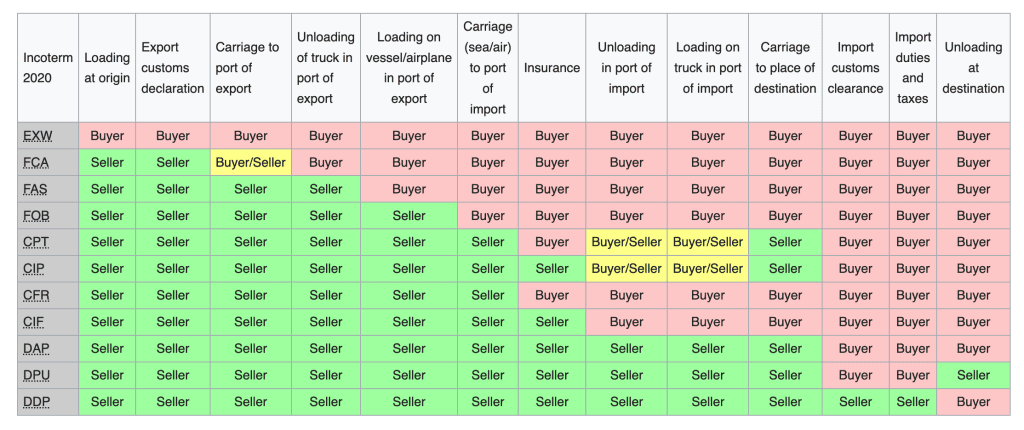
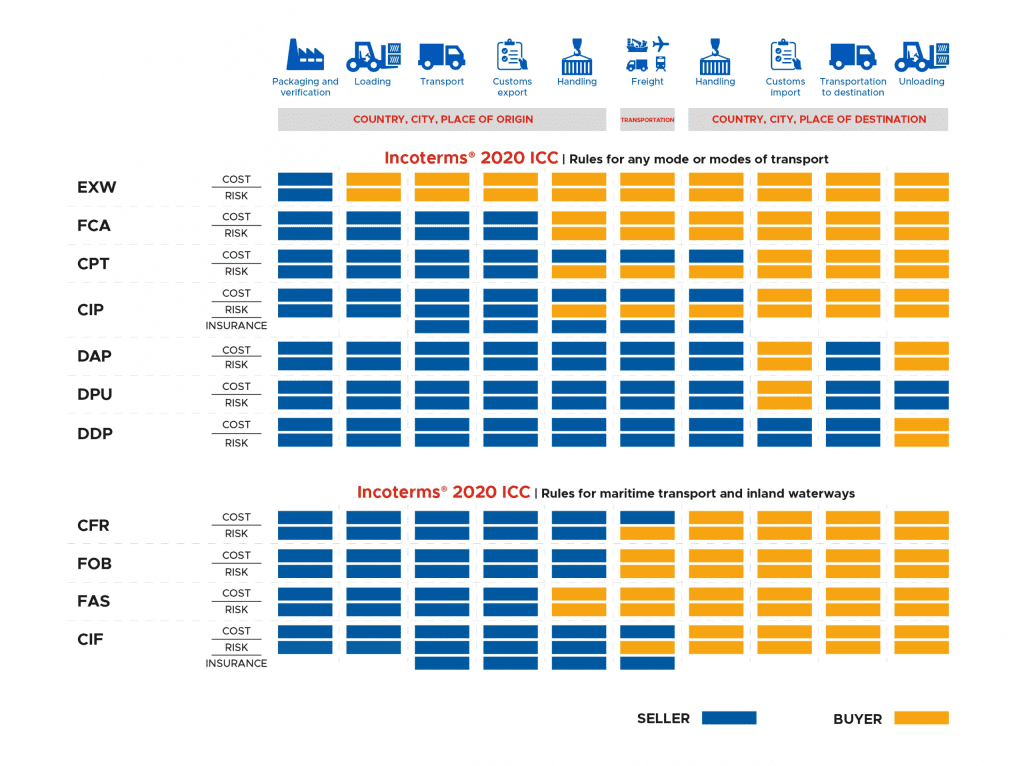
Incoterms contracts are divided into 4 groups according to their characteristics, these are groups E, F, C and D.
-
Group E - shipment, transfer of obligations - at the place of dispatch. The seller is obliged to provide the goods to the buyer directly at the manufacturing plant, his warehouse, the seller does not perform customs clearance of the goods; The seller is not responsible for loading the goods onto the vehicle; EXW.
-
Group F - the main carriage is not paid by the seller, the transfer of obligations at the departure terminals for the main carriage. The seller undertakes to place the goods at the disposal of a carrier hired by the buyer himself; FCA, FAS, FOB.
-
Group C - the main carriage is paid by the seller, the transfer of obligations is at the terminals of arrival for the main carriage. The seller is obliged to conclude a contract for the carriage of goods, but without assuming the risk of its accidental loss or damage to the goods; CFR, CIF, CPT, CIP.
-
Group D - arrival, transfer of obligations from the buyer, full delivery. The seller bears all shipping costs and assumes all risks until the goods are delivered to the country of destination; DAT, DAP, DDP.
EXW (ex works)
The goods are taken by the buyer from the seller's warehouse specified in the contract, payment of export duties is charged to the buyer.
FCA (free carrier)
The goods are delivered to the main carrier of the customer to the departure terminal specified in the contract, the export duties are paid by the seller.
FAS(Free Alongside Ship)
The goods are delivered to the buyer's ship, the port of loading is indicated in the contract, the buyer pays for transshipment and loading.
FOB(Free On Board)
The goods are shipped to the ship of the buyer, the transshipment is paid by the seller.
CFR(Cost and Freight)
The goods are delivered to the buyer's destination port specified in the contract, the buyer pays for the insurance of the main transportation, unloading and transshipment.
CİF(Cost, Insurance and Freight)
Same as CFR, but the main carriage is insured by the seller.
CPT(Carriage Paid To)
The goods are delivered to the main carrier of the customer, the main transportation to the arrival terminal specified in the contract is paid by the seller, the buyer bears the insurance costs, import customs clearance and delivery from the arrival terminal of the main carrier is carried out by the buyer.
CİP(Carriage And Insurance Paid To)
Same as CPT, but the main carriage is insured by the seller.
DDP(Delivered Duty Paid)
The goods are delivered to the customer at the destination specified in the contract, cleared of all customs duties and risks.
DAT(Delivered at Terminal)
Delivery to the import customs terminal specified in the contract is paid, that is, export payments and the main transportation, including insurance, are paid by the seller, customs clearance for import is carried out by the buyer.
DAP(Delivered at Place)
Delivery to the destination specified in the contract, import duties and local taxes are paid by the buyer.